Portal:Ancient Egypt
|
THE ANCIENT EGYPT PORTAL
Showcased content about Ancient Egypt Ancient Egypt was a civilization of ancient Northeast Africa. It was concentrated along the lower reaches of the Nile River, situated in the place that is now the country Egypt. Ancient Egyptian civilization followed prehistoric Egypt and coalesced around 3100 BC (according to conventional Egyptian chronology) with the political unification of Upper and Lower Egypt under Menes (often identified with Narmer). The history of ancient Egypt unfolded as a series of stable kingdoms interspersed by periods of relative instability known as “Intermediate Periods.” The various kingdoms fall into one of three categories: the Old Kingdom of the Early Bronze Age, the Middle Kingdom of the Middle Bronze Age, or the New Kingdom of the Late Bronze Age. Ancient Egypt reached the pinnacle of its power during the New Kingdom, ruling much of Nubia and a sizable portion of the Levant. After this period, it entered an era of slow decline. During the course of its history, Ancient Egypt was invaded or conquered by a number of foreign powers, including the Hyksos, the Nubians, the Assyrians, the Achaemenid Persians, and the Macedonians under Alexander the Great. The Greek Ptolemaic Kingdom, formed in the aftermath of Alexander's death, ruled until 30 BC, when, under Cleopatra, it fell to the Roman Empire and became a Roman province. Egypt remained under Roman control until the 640s AD, when it was conquered by the Rashidun Caliphate. The success of ancient Egyptian civilization came partly from its ability to adapt to the conditions of the Nile River valley for agriculture. The predictable flooding and controlled irrigation of the fertile valley produced surplus crops, which supported a more dense population, and social development and culture. With resources to spare, the administration sponsored mineral exploitation of the valley and surrounding desert regions, the early development of an independent writing system, the organization of collective construction and agricultural projects, trade with surrounding regions, and a military intended to assert Egyptian dominance. Motivating and organizing these activities was a bureaucracy of elite scribes, religious leaders, and administrators under the control of a pharaoh, who ensured the cooperation and unity of the Egyptian people in the context of an elaborate system of religious beliefs.[1] The many achievements of the ancient Egyptians include the quarrying, surveying, and construction techniques that supported the building of monumental pyramids, temples, and obelisks; a system of mathematics, a practical and effective system of medicine, irrigation systems, and agricultural production techniques, the first known planked boats, Egyptian faience and glass technology, new forms of literature, and the earliest known peace treaty, made with the Hittites. Ancient Egypt has left a lasting legacy. Its art and architecture were widely copied, and its antiquities were carried off to far corners of the world. Its monumental ruins have inspired the imaginations of travelers and writers for millennia. A newfound respect for antiquities and excavations in the early modern period by Europeans and Egyptians has led to the scientific investigation of Egyptian civilization and a greater appreciation of its cultural legacy. (Full article...) Selected article - Sirius is the brightest star in the night sky. Its name is derived from the Greek word Σείριος (Latin script: Seirios), meaning lit. 'glowing' or 'scorching'. The star is designated α Canis Majoris, Latinized to Alpha Canis Majoris, and abbreviated α CMa or Alpha CMa. With a visual apparent magnitude of −1.46, Sirius is almost twice as bright as Canopus, the next brightest star. Sirius is a binary star consisting of a main-sequence star of spectral type A0 or A1, termed Sirius A, and a faint white dwarf companion of spectral type DA2, termed Sirius B. The distance between the two varies between 8.2 and 31.5 astronomical units as they orbit every 50 years. Sirius appears bright because of its intrinsic luminosity and its proximity to the Solar System. At a distance of 2.64 parsecs (8.6 ly), the Sirius system is one of Earth's nearest neighbours. Sirius is gradually moving closer to the Solar System; it is expected to increase in brightness slightly over the next 60,000 years to reach a peak magnitude of −1.68. Coincidentally, at about the same time, Sirius will take its turn as the southern Pole Star, around the year 66,270 AD. In that year, Sirius will come to within 1.6 degrees of the south celestial pole. This is due to axial precession and proper motion of Sirius itself which moves slowly in the SSW direction, so it will be visible from the southern hemisphere only. (Full article...)Selected picture
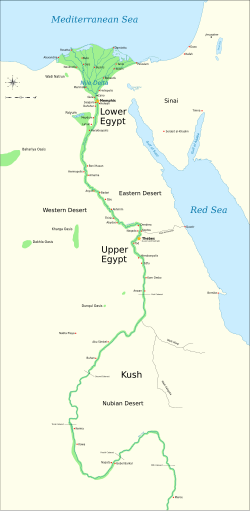
In antiquity, Ancient Egypt was divided into two lands: Upper Egypt and Lower Egypt. To the south, it was bounded by the land of Kush, and to the East, the levant. Surrounded by harsh deserts, the river Nile was the lifeline of this ancient civilization. Did you know...
News5th September 2018. Rock-cut Tomb discovered in a 4,000-year-old Elite Cemetery August 2018: in the tomb of the mayor of Memphis Ptahmose who dates around 1300 BC was found well preserved cheese, more than 3000 years old. [1] Selected biography -Thutmose I (sometimes read as Thutmosis or Tuthmosis I, Thothmes in older history works in Latinized Greek; meaning "Thoth is born") was the third pharaoh of the 18th Dynasty of Egypt. He received the throne after the death of the previous king, Amenhotep I. During his reign, he campaigned deep into the Levant and Nubia, pushing the borders of Egypt farther than ever before in each region. He also built many temples in Egypt, and a tomb for himself in the Valley of the Kings; he is the first king confirmed to have done this (though Amenhotep I may have preceded him). Thutmose I's reign is generally dated to 1506–1493 BC, but a minority of scholars—who think that astrological observations used to calculate the timeline of ancient Egyptian records, and thus the reign of Thutmose I, were taken from the city of Memphis rather than from Thebes—would date his reign to 1526–1513 BC. He was succeeded by his son Thutmose II, who in turn was succeeded by Thutmose II's sister, Hatshepsut. (Full article...)General imagesThe following are images from various ancient Egypt-related articles on Wikipedia.
Related portalsWikiProjectsMain topics
Notable Pharaohs
CategoriesRecognized content
Featured articles
Featured listsGood articles
Did you know? articles
Featured pictures
In the News articlesMain page featured articles
Main page featured listsPicture of the day pictures
Things to do
WikimediaThe following Wikimedia Foundation sister projects provide more on this subject:
Sources
Discover Wikipedia using portals |