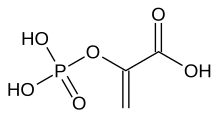
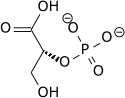
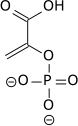
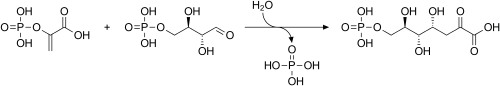Acide phosphoénolpyruvique - Phosphoenolpyruvic acid
|
|
|
|
| Des noms | |
|---|---|
|
Nom IUPAC préféré
Acide 2-(Phosphonooxy)prop-2-énoïque |
|
| Autres noms
Acide phosphoénolpyruvique, PEP
|
|
| Identifiants | |
|
Modèle 3D ( JSmol )
|
|
| ChEBI | |
| ChemSpider | |
| Banque de médicaments | |
| Carte d'information de l'ECHA |
100.004.830 |
|
CID PubChem
|
|
| UNII | |
|
Tableau de bord CompTox ( EPA )
|
|
|
|
|
|
| Propriétés | |
| C 3 H 5 O 6 P | |
| Masse molaire | 168.042 |
|
Sauf indication contraire, les données sont données pour les matériaux dans leur état standard (à 25 °C [77 °F], 100 kPa). |
|
|
|
|
| Références de l'infobox | |
Le phosphoénolpyruvate ( 2-phosphoénolpyruvate , PEP ) est l' ester dérivé de l' énol du pyruvate et du phosphate . Il existe sous forme d' anion . Le PEP est un intermédiaire important en biochimie . Il possède la liaison phosphate la plus énergétique trouvée (-61,9 kJ/mol) dans les organismes, et est impliqué dans la glycolyse et la gluconéogenèse . Chez les plantes, il est également impliqué dans la biosynthèse de divers composés aromatiques , et dans la fixation du carbone ; chez les bactéries, il est également utilisé comme source d'énergie pour le système phosphotransférase .
En glycolyse
La PEP est formée par l'action de l' enzyme énolase sur l' acide 2-phosphoglycérique . Le métabolisme du PEP en acide pyruvique par la pyruvate kinase (PK) génère de l' adénosine triphosphate (ATP) via une phosphorylation au niveau du substrat . L'ATP est l'une des principales devises de l'énergie chimique au sein des cellules .
| 2-phospho- D -glycerate | Enolase | phosphoénolpyruvate | Pyruvate kinase | pyruvate | ||
|
|

|
||||
| H 2 O | ADP | ATP | ||||
|
|
|||||
| H 2 O | ||||||
Composé C00631 dans la base de données KEGG Pathway. Enzyme 4.2.1.11 à KEGG Pathway Database. Composé C00074 dans la base de données KEGG Pathway. Enzyme 2.7.1.40 dans la base de données KEGG Pathway. Composé C00022 dans la base de données Pathway KEGG .
Dans la néoglucogenèse
Le PEP est formé à partir de la décarboxylation de l' oxaloacétate et de l' hydrolyse d'une molécule de guanosine triphosphate . Cette réaction est catalysée par l'enzyme phosphoénolpyruvate carboxykinase (PEPCK). Cette réaction est une étape limitante de la néoglucogenèse :
- GTP + oxaloacétate → GDP + phosphoénolpyruvate + CO 2
Carte interactive des sentiers
Cliquez sur les gènes, les protéines et les métabolites ci-dessous pour accéder aux articles respectifs.
Dans les plantes
Le PEP peut être utilisé pour la synthèse du chorismate par la voie shikimate . Le chorismate peut ensuite être métabolisé en acides aminés aromatiques ( phénylalanine , tryptophane et tyrosine ) et autres composés aromatiques. La première étape est lorsque le phosphoénolpyruvate et l' érythrose-4-phosphate réagissent pour former le 3-désoxy-D-arabinoheptulosonate-7-phosphate (DAHP), dans une réaction catalysée par l'enzyme DAHP synthase .
De plus, dans les plantes en C 4 , le PEP sert de substrat important dans la fixation du carbone . L'équation chimique, catalysée par la phosphoénolpyruvate carboxylase (PEP carboxylase), est :
- PPE + HCO−
3 → oxaloacétate
Les références
- ^ Berg, Jeremy M.; Tymoczko, Stryer (2002). Biochimie (5e éd.). New York : WH Freeman and Company . ISBN 0-7167-3051-0.
- ^ Nelson, DL; Cox, MM "Lehninger, Principes de biochimie" 3e éd. Worth Publishing: New York, 2000. ISBN 1-57259-153-6 .
- ^ "InterPro: IPR008209 Phosphoenolpyruvate carboxykinase, utilisant GTP" . Récupéré le 2007-08-17 .
- ^ "BioCarta - Tracer les chemins de la vie" . Récupéré le 2007-08-17 .